Haptic Enabled Smart Goggles for Visually Impaired
🎯 Objective
To design and build a wearable smart goggle system that enables visually impaired individuals to navigate complex urban environments independently and safely using real-time feedback through computer vision and sensor fusion. PRODIGY is a lightweight wearable device offering visual place recognition, traffic light detection, obstacle avoidance, and audio & haptic feedback.
💡 Problem Statement
Navigating busy cities is a major challenge for the blind. Traditional aids like canes and guide dogs are limited:
- Lack of feedback in noisy environments
- Insufficient awareness of surroundings
- Inconvenient or unintuitive smart devices
🧱 System Architecture
The development incorporates cutting-edge AI and embedded systems technologies:
Vision System
- Sony IMX500 camera with on-sensor AI accelerator for object detection
- YOLOv8 model trained on self-collected Manhattan dataset
- Real-time traffic light and obstacle detection
- Visual place recognition for navigation
Embedded Computing
- Raspberry Pi as core compute platform
- Hailo-8 AI accelerator (planned for crosswalk detection)
- Custom software stack optimized for real-time inference
- Power management for 8-10 hours battery life
Feedback Systems
- Haptic motors integrated into goggle frame
- Audio feedback through standard earphones
- GPS navigation with directional guidance
- Customizable vibration and audio responses
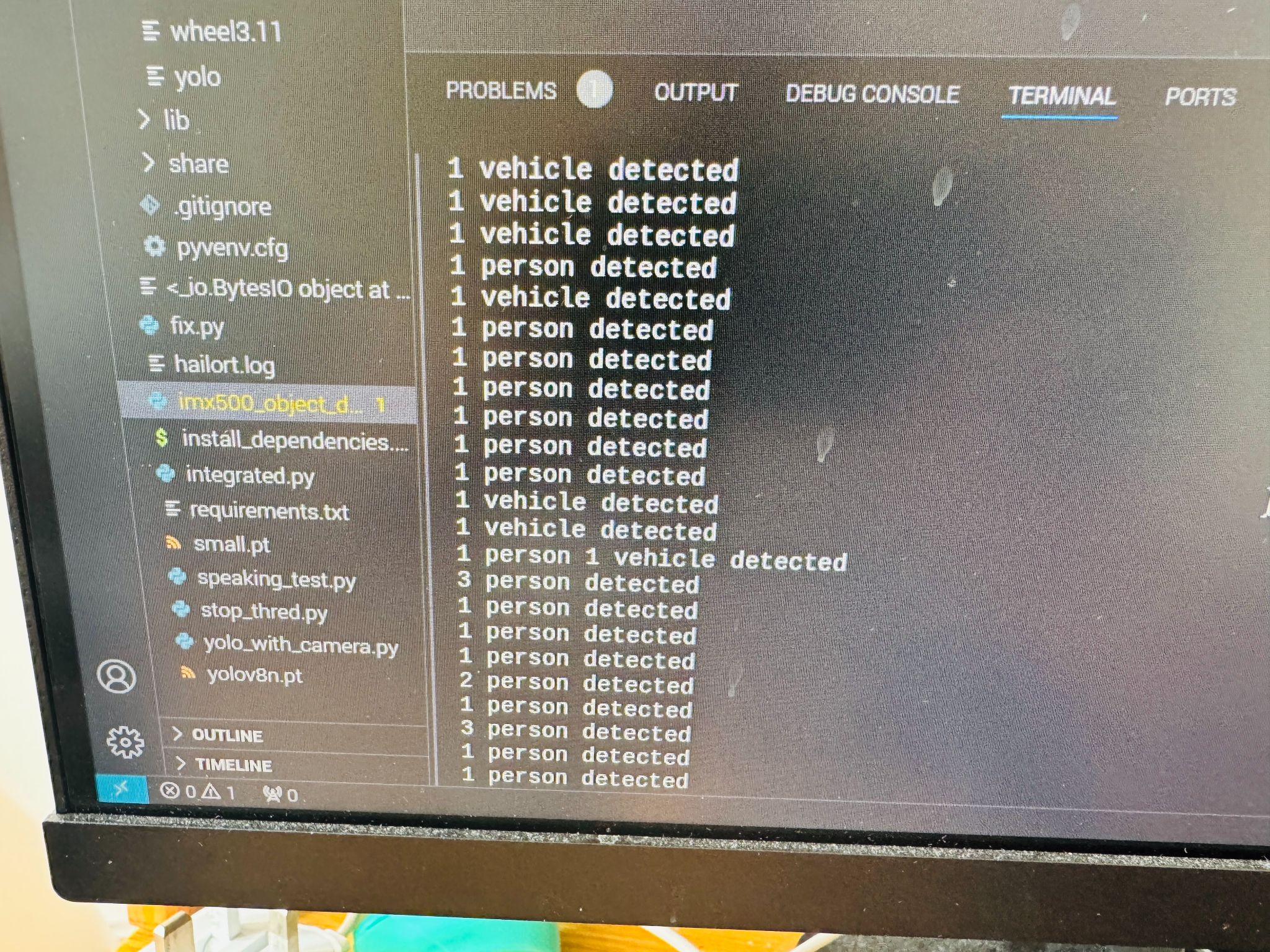
YOLOv8 model detecting traffic lights, pedestrians, and urban obstacles in real-time
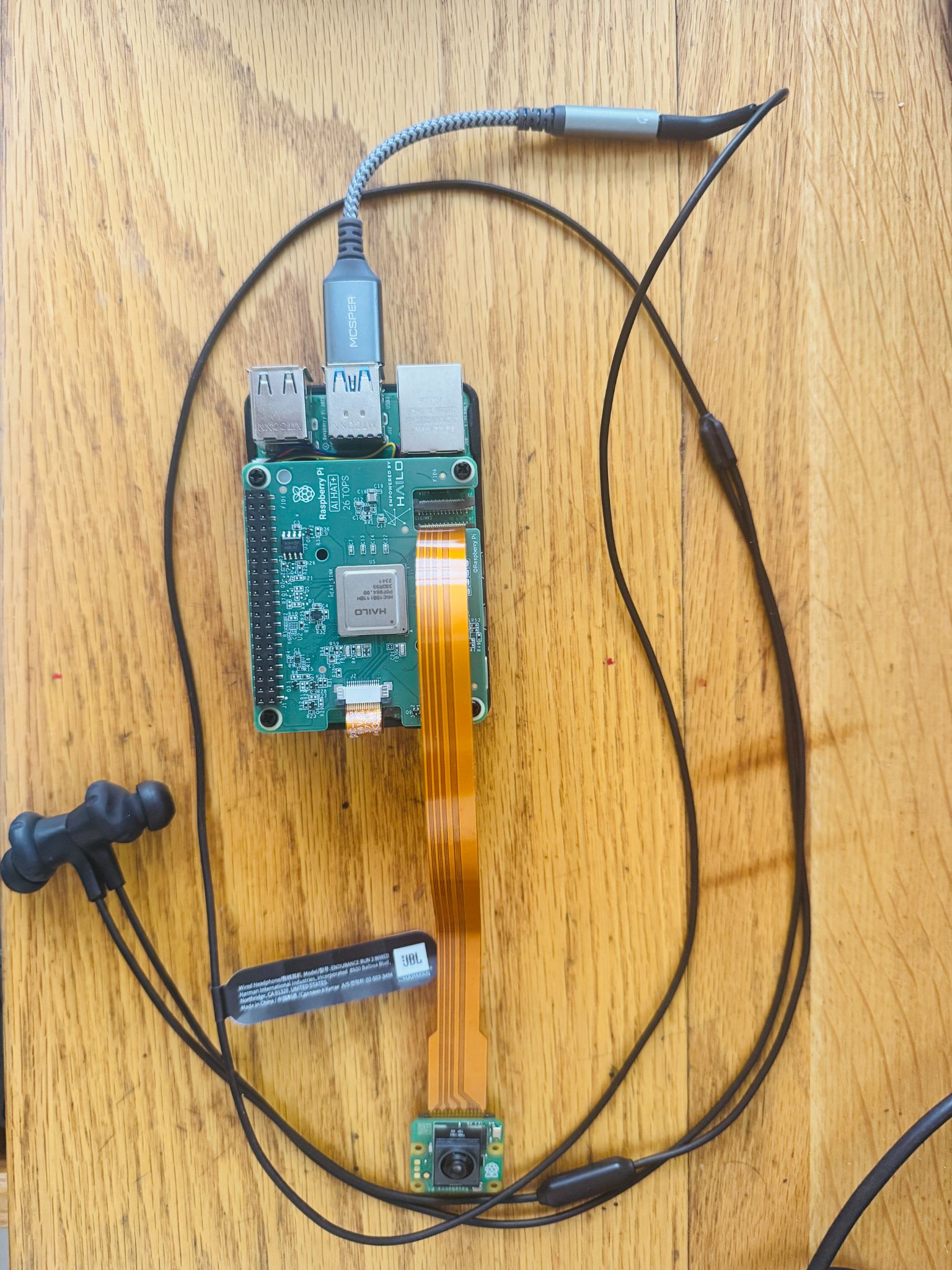
Raspberry Pi, camera system, and haptic feedback components integrated into the goggle frame

Demonstration of the complete system with real-time object detection, haptic feedback, and audio guidance for visually impaired navigation
🧠 Key Features
Object Detection
Real-time detection of people, crosswalks, vehicles, poles, bikes, and other urban obstacles using advanced computer vision
Red Light Recognition
YOLOv8 model trained on self-collected Manhattan dataset for accurate traffic light detection
Obstacle Avoidance
Proximity sensing and alerting based on surroundings with directional haptic feedback
Audio + Haptics
Dual feedback system via earphones and vibration motors integrated in the frame
GPS Navigation
Directional guidance for urban mobility with step-by-step auditory instructions
Long Battery Life
8–10 hours of continuous use with power-saving mode optimization
🔧 Challenges & Solutions
CPU Limitations
Raspberry Pi bottlenecks for heavy real-time inference - addressed through model optimization and AI accelerators
Model Quantization
Hardware resource constraints on Hailo - ongoing optimization of neural network architectures
Training Data
Collection and labeling across multiple urban environments - custom Manhattan dataset creation
📈 Impact and Applications
This assistive technology project addresses critical mobility challenges for visually impaired individuals in urban environments:
Accessibility Innovation
Intuitive feedback system replacing complexity with meaningful, actionable guidance
Safety Enhancement
Real-time obstacle detection and traffic light recognition for safer navigation
User-Centered Design
Lightweight, comfortable, and intuitive design based on user feedback and testing
🛡️ Regulatory Compliance
Medical Device Standards
- ISO 13485: Medical device quality management system
- IEC 62304: Medical device software lifecycle processes
- IEC 60601-1: Electrical safety for medical equipment
- ISO/IEC 27001 & HIPAA: Information and health data security
🔮 Future Roadmap
- ✅ Crosswalk Detection via Hailo AI accelerator (pending hardware compatibility)
- 🌍 Vision Language Model (VLM) Integration for full-scene understanding
- 📞 SOS Call Feature & Location Sharing for emergency situations
- 🧠 Integration with Neural Implants (exploratory research)
- 🔋 Partnership with battery & AI chip manufacturers for enhanced performance
- 🌐 Expansion into global assistive technology markets
🪞 Reflection and Conclusion
This project provided deep insight into how AI and robotics can directly improve lives, especially for vulnerable populations. From dataset collection in Manhattan to training YOLOv8 models, and integrating real-time haptic and auditory feedback, I was involved in both hardware prototyping and AI system design.
The experience exposed me to regulatory frameworks, real-world deployment constraints, and the critical importance of user-centered design in accessibility technology. PRODIGY represents a significant step forward in assistive technology, combining cutting-edge AI with intuitive human-computer interaction to address real-world challenges faced by visually impaired individuals.
The project demonstrates the potential for AI-powered wearable devices to serve as meaningful assistive tools, replacing complexity with intuitive feedback that enhances independence and safety in urban navigation.