Autonomous Maze Solving Robot Simulation
Abstract
This project implements an autonomous maze-solving robot simulation as the final project for Robot Vision class. The objective was to locate a specific target image within a maze whose walls consisted of various image patterns from a predefined pool. The challenge involved finding the shortest path to the target while navigating through a complex visual environment. Our approach utilized VLAD (Vector of Locally Aggregated Descriptors) and SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) features combined with Ball Tree algorithms for efficient navigation and real-time map updating for precise localization.
Methodology
The development process incorporated advanced computer vision and robotics techniques for autonomous navigation:
Maze Mapping and Exploration
- Sequential frame numbering during exploration phase
- Keystroke-based maze mapping construction
- Complete maze layout reconstruction from exploration data
- Target location identification within exploration frames
Computer Vision Implementation
- VLAD (Vector of Locally Aggregated Descriptors) for image representation
- SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) for feature detection
- Ball Tree algorithm for efficient nearest neighbor search
- Image pattern recognition on maze walls
Navigation and Localization
- Real-time map updating during navigation
- Shortest path calculation algorithms
- Live localization system integration
- Visual pattern matching for position estimation
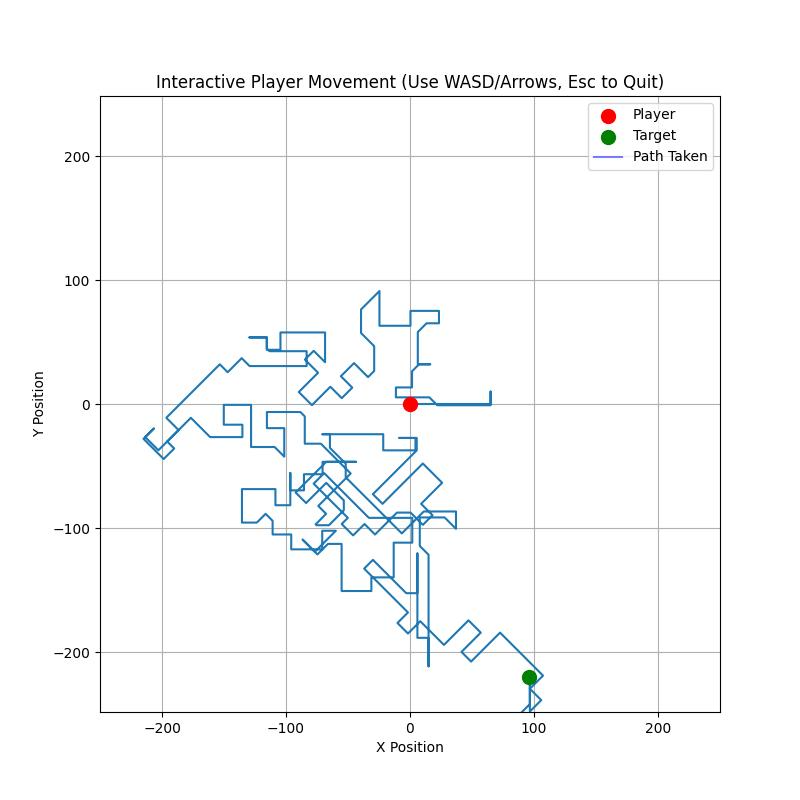
Maze mapping from the maze exploration keystrokes
Keystrokes in sequential order to explore the maze
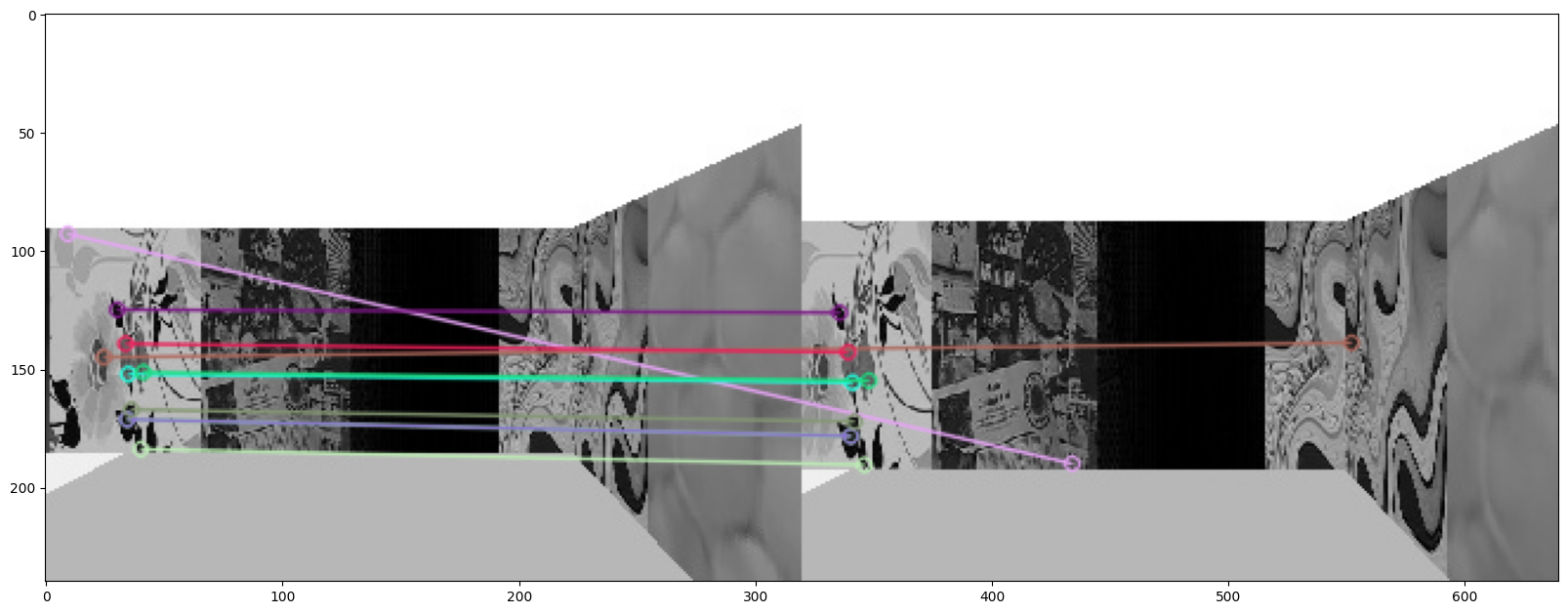
Matching of the target image to the images in the exploration POVs
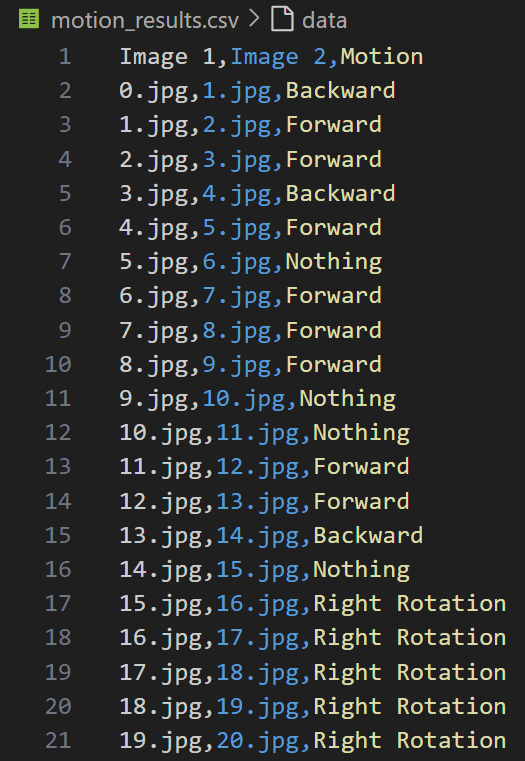
Parsing of the exploration data files to extract relevant information for navigation
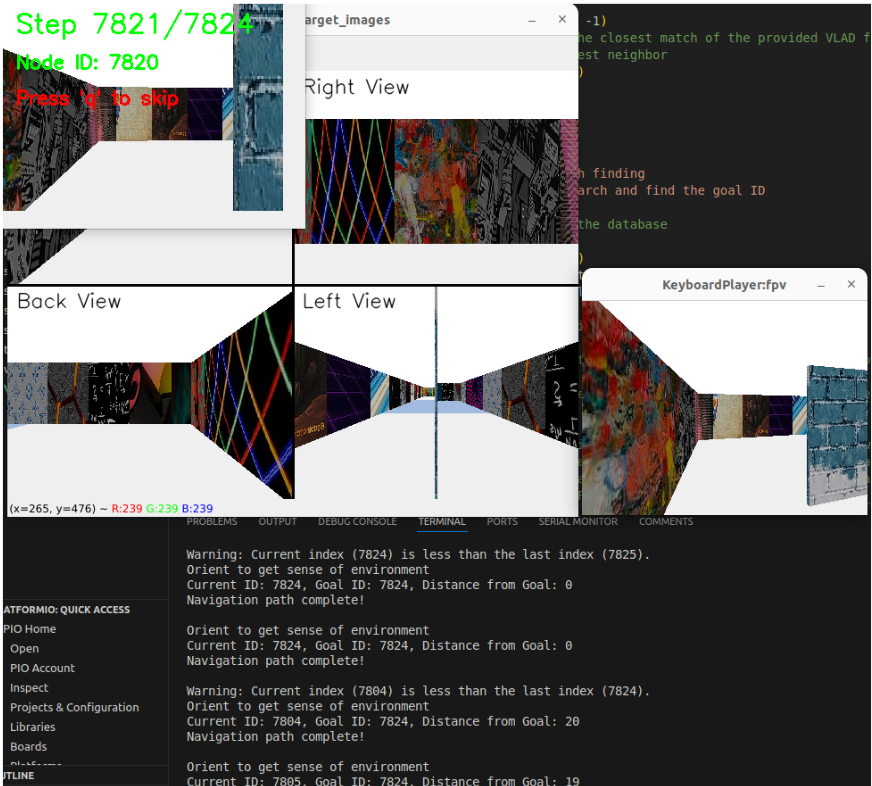
The simulation demonstrates the robot navigating through a maze with image-pattern walls to locate the target pattern using computer vision techniques
Key Innovations
VLAD + SIFT Integration
Advanced feature extraction using VLAD descriptors combined with SIFT features for robust image pattern recognition
Ball Tree Navigation
Efficient nearest neighbor search using Ball Tree algorithm for real-time pattern matching and localization
Live Map Update
Real-time map construction and updating based on exploration data and visual feedback
Shortest Path Optimization
Intelligent path planning algorithms to find the most efficient route to the target location
Technical Approach and Implementation
Our solution to the autonomous maze navigation challenge involved a multi-phase approach combining computer vision and intelligent path planning:
Phase 1: Exploration and Mapping
- Recorded keystroke sequences during manual exploration phase
- Sequential numbering of exploration frames for reference
- Construction of complete maze map from exploration data
- Identification of target pattern location within numbered frames
Phase 2: Visual Feature Extraction
- Implementation of SIFT algorithm for keypoint detection and description
- VLAD encoding for compact image representation
- Creation of visual vocabulary from wall pattern images
- Feature database construction for pattern matching
Phase 3: Navigation and Localization
- Ball Tree implementation for efficient similarity search
- Real-time localization using visual pattern matching
- Dynamic map updating during navigation
- Shortest path calculation to target location
Academic Achievement
Successfully completed as final project for Robot Vision class, demonstrating mastery of computer vision concepts
Computer Vision Innovation
Novel application of VLAD and SIFT features for maze navigation and pattern recognition
Autonomous Systems
Foundation for autonomous navigation systems in complex visual environments
Future Enhancements
- Integration with real-world robotic platforms for physical maze navigation
- Implementation of deep learning approaches for improved pattern recognition
- Extension to dynamic environments with moving obstacles
- Multi-robot coordination for collaborative maze exploration
- Real-time SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) integration
Conclusion
The Autonomous Maze Solving Robot Simulation successfully demonstrates the integration of computer vision techniques with intelligent navigation algorithms. By combining VLAD and SIFT features with Ball Tree search algorithms, the system achieves robust pattern recognition and efficient pathfinding in complex visual environments. The project showcases the practical application of advanced computer vision concepts in autonomous robotics, providing a solid foundation for real-world navigation systems. The live map updating and localization capabilities demonstrate the system's adaptability and precision in dynamic exploration scenarios.